10866.
Ternary search in array
Ternary
search is a divide and conquer algorithm that can be used to find an element in
an array. It is similar to binary search but in this algorithm, we divide the
given array into three equal parts and determine which has the key (searched
element).
Sorted array of n integers is given. You must answer q queries: whether the given number x is in the array.
Input. First line contains two numbers n and q (n, q ≤ 106). Second line
contains n integers sorted in
increasing order. Each of the next q lines
contains value of x. The numbers in
array do not exceed 109 by absolute value.
Output. For each value of
x print on a separate line “YES” if x is present in array and “NO”
otherwise.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
6 3 2 4 4 8 11 14 10 4 2 |
NO YES YES |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
8 4 -8 -8 -1 1 3 4 6 8 4 10 -4 -8 |
YES NO NO YES |
SOLUTION
ternary search
Algorithm analysis
In this problem one must find a
number in a sorted array. Let’s do it using ternary search.
Let the element x be
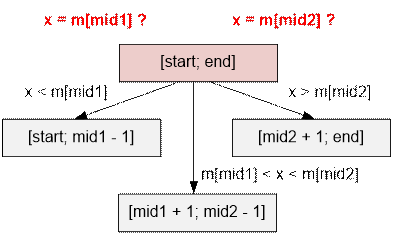
searched in the array m in the interval [start; end]. Divide
the segment [start; end] into three equal parts. Let
·
mid1 = start + (end – start)
/ 3;
·
mid2 = end – (end – start)
/ 3;
If x equals to m[mid1] or m[mid2], then number x is found, we return 1. Otherwise, depending on the following conditions, we
continue the search in one of the intervals:
·
if x < m[mid1], then x lies on segment [start; mid1 – 1].
·
if m[mid1] < x < m[mid2], then x lies on segment [mid1 + 1; mid2 – 1].
·
if x > m[mid2], then x lies on segment [mid2 + 1; end].
Algorithm realization
Declare the array.
#define MAX 1000001
int m[MAX];
Function my_ternary_search returns 1 if element x is present in the array m[start; end].
int my_ternary_search(int* m, int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start < end)
{
int mid1 = start + (end - start) / 3;
int mid2 =
end - (end - start) / 3;
if (x == m[mid1])
return 1;
if (x == m[mid2])
return 1;
if (x < m[mid1])
end = mid1 - 1;
else if (x < m[mid2])
{
start = mid1 + 1;
end = mid2 - 1;
}
else
start = mid2 + 1;
}
return x == m[start];
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &m[i]);
Sequentially process q queries using ternary search.
for (i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
if
(my_ternary_search(m, 0, n - 1, x))
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
}
Java realization
import
java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
public static int m[];
public static boolean my_ternary_search(int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start < end)
{
int mid1 = start + (end - start) / 3;
int mid2 = end - (end - start) / 3;
if (x == m[mid1]) return true;
if (x == m[mid2]) return true;
if (x < m[mid1])
end = mid1 - 1;
else if (x < m[mid2])
{
start = mid1 + 1;
end = mid2 - 1;
}
else
start = mid2 + 1;
}
return x == m[start];
}
public static void main(String []args)
{
//Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
FastScanner con =
new FastScanner(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));;
int n = con.nextInt();
int q = con.nextInt();
m = new int [n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
int x = con.nextInt();
if (my_ternary_search(0, n - 1, x))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
//con.close();
}
}
class FastScanner
{
private BufferedReader br;
private StringTokenizer st;
public FastScanner(InputStreamReader reader)
{
br = new BufferedReader(reader);
}
public String next()
{
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens())
{
try
{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt()
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public double nextDouble()
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public void close() throws Exception
{
br.close();
}
}